Other Classes
SoLoud::Bus
The mixing busses are a special case of an audio stream. They are a kind of audio stream that plays other audio streams. Mixing bus can also play other mixing busses. Like any other audio stream, mixing bus has volume, panning and filters.
Only one instance of a mixing bus can play at the same time, however; trying to play the same bus several times stops the earlier instance.
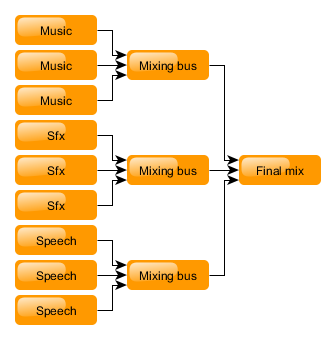
While a mixing bus doesn't generate audio by itself, playing it counts against the maximum number of concurrent streams.
Mixing busses are protected by default (i.e, won't stop playing if maximum number of concurrent streams is reached), and also marked as "must tick" (i.e, will always be present in the active voices list).
To play a stream through the mixing bus, use the bus play() command.
int bushandle = gSoloud.play(gBus); // Play the bus
gSoloud.setVolume(bushandle, 0.5f); // Set bus volume
int fxhandle = gBus.play(gSoundEffect); // Play sound effect through bus
gSoloud.setVolume(fxhandle, 0.5f); // set sound effect volume
When chaining busses care should be taken, as resampling will offset the output by a number of samples. Point sampling by 0, linear by 1, and higher resamplers with higher number of samples.
Bus.setChannels()
Set the number of channels this bus should handle. Defaults to 2 (stereo).
gBus.setChannels(1); // set to mono
Bus.play()
Equivalent of soloud.play(), but plays the sound source through the bus instead of at "global" scope.
Bus.playClocked()
Equivalent of soloud.playClocked(), but plays the sound source through the bus instead of at "global" scope.
Bus.play3d()
Equivalent of soloud.play3d(), but plays the sound source through the bus instead of at "global" scope.
Bus.play3dClocked()
Equivalent of soloud.play3dClocked(), but plays the sound sounce through the bus instead of at "global" scope.
Bus.setVisualizationEnable()
Enable (or disable) gathering of visualization wave data from this bus.
Bus.calcFFT()
Calculates FFT of the sound currently playing through this bus, and returns a pointer to the result.
float * fft = fxbus.calcFFT();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
drawline(0, i, fft[i] * 32, i);
The FFT data has 256 floats, from low to high frequencies.
SoLoud performs a mono mix of the audio, passes it to FFT, and then calculates the magnitude of the complex numbers for application to use. For more advanced FFT use, SoLoud code changes are needed.
The returned pointer points at a buffer that's around as long as the bus object exists, but the data is only updated when calcFFT() is called.
For the FFT to work, you also need to enable visualization with the Bus.setVisualizationEnable() call. Otherwise the source data for the FFT calculation will not be gathered.
Bus.getWave()
Gets 256 samples of the sound currently playing through this bus, and returns a pointer to the result.
float * wav = speechbus.getWave();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
drawline(0, i, wav[i] * 32, i);
The returned pointer points at a buffer that's around as long as the bus object exists, but the data is only updated when getWave() is called. The data is the same that is used to generate visualization FFT data.
For this function to work properly, you also need enable visualization with the Bus.setVisualizationEnable() call. Otherwise the source data will not be gathered, and the result is undefined (probably zero).
Bus.getApproximateVolume()
Gets the approximate volume for output per output channel (i.e, per speaker). Returns zero for invalid parameters.
float ch1 = gBus.getApproximateVolume(0);
float ch2 = gBus.getApproximateVolume(1);
printf("Volume is %3.3f %3.3f", ch1, ch2);
Visualization needs to be enabled for this function to work.
Bus.setLooping(), Bus.setLoopPoint(), Bus.getLoopPoint()
Trying to change the looping state of a bus has no effect.
Bus.stop()
This is equivalent of calling soloud.stopAudioSource() with the sound source.
Bus.setFilter()
As with any other audio source, you can attach filters to busses.
gSfxBus.setFilter(0, &gEnvironment);
Bus.setInaudibleBehavior()
Set the inaudible behavior of the sound. By default, if a sound is inaudible, it's paused, and will resume when it becomes audible again. With this function you can tell SoLoud to either kill the sound if it becomes inaudible, or to keep ticking the sound even if it's inaudible.
// Kill off the sfx if they're not heard.
gSfxBus.setInaudibleBehavior(false, true);
Bus.setVolume()
Set the default volume of the bus.
gMusicBus.setVolume(11);
Bus.annexSound()
Move live audio stream under this bus. This can be useful if you have some heavy filtering under one bus and want to move playing sounds in and out of the bus.
gTunnelBus.annexSound(sfxBus);
Bus.getActiveVoiceCount()
Returns the number of concurrent sounds that are playing through this bus at the moment.
if (sfxbus.getActiveVoiceCount() == 0) enjoy_the_silence();
Inherited 3d audio interfaces
Like all other audio sources, the bus inherits the 3d audio interfaces. Please refer to the 3d audio chapter for details on:
- Bus.set3dMinMaxDistance()
- Bus.set3dAttenuation()
- Bus.set3dDopplerFactor()
- Bus.set3dProcessing()
- Bus.set3dListenerRelative()
- Bus.set3dDistanceDelay()
- Bus.set3dCollider()
- Bus.set3dAttenuator()
Copyright©2013-2020 Jari Komppa
