Miscellaneous
Soloud.getStreamTime()
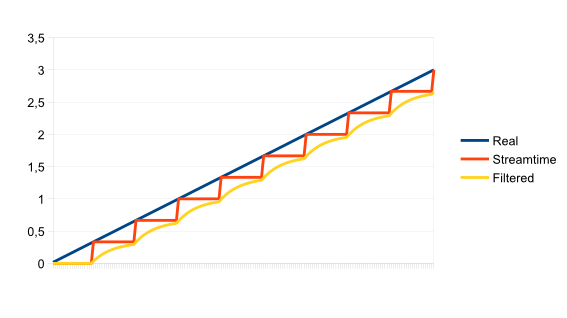
The getStreamTime function can be used to get the current play position, in seconds.
double t = soloud.getStreamTime(h); // get time
if (t == hammertime) hammer();
Note that time is a double instead of float because float will cause precision problems within 24 hours of playing, and eventually, in about 6 days, will cause the "time" to stop.
Also note that the granularity is likely to be rather high (possibly around 45ms), so using this as the sole clock source for animation will lead to rather low framerate (possibly around 20Hz). To fix this, either use some other clock source and only sync with the stream time occasionally, or use some kind of low-pass filter, such as..
mytime = (mytime * 9 + soloud.getStreamTime(h)) / 10;
While not perfect, that's way better than using the stream time directly.
Soloud.getStreamPosition()
Gets the stream position of a specific voice handle.
if (soloud.getStreamPosition(music) > 30) past_the_good_bit();
Soloud.isValidVoiceHandle()
The isValidVoiceHandle function can be used to check if a handle is still valid.
if (!soloud.isValidVoiceHandle(h)) delete foobar;
If the handle is invalid, the isValidVoiceHandle will return 0.
Soloud.getActiveVoiceCount()
Returns the number of concurrent sounds that are playing at the moment.
if (soloud.getActiveVoiceCount() == 0) enjoy_the_silence();
Soloud.countAudioSource()
Returns the number of concurrent soudns that are playing a specific audio source.
if (soloud.countAudioSource(cheer) == 3) three_cheers();
Soloud.getVoiceCount()
Returns the number of voices the application has told SoLoud to play.
if (soloud.getVoiceCount() > 1000) lots_of_voices();
Soloud.setMaxActiveVoiceCount(), Soloud.getMaxActiveVoiceCount()
Get or set the current maximum active voice count. If voice count is higher than the maximum active voice count, SoLoud will pick the ones with the highest volume to actually play.
int voices = gSoloud.getMaxActiveVoiceCount();
if (fps < 60 && voices > 16)
gSoloud.setMaxActiveVoiceCount(voices / 2);
Soloud.setGlobalFilter()
Sets, or clears, the global filter.
soloud.setGlobalFilter(0, &echochamber); // set first filter
Setting the global filter to NULL will clear the global filter. The default maximum number of global filters active is 4, but this can be changed in a global constant in soloud.h (and rebuilding SoLoud).
Soloud.calcFFT()
Calculates FFT of the currently playing sound (post-clipping) and returns a pointer to the result.
float * fft = soloud.calcFFT();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
drawline(0, i, fft[i] * 32, i);
The FFT data has 256 floats, from low to high frequencies.
SoLoud performs a mono mix of the audio, passes it to FFT, and then calculates the magnitude of the complex numbers for application to use. For more advanced FFT use, SoLoud code changes are needed.
The returned pointer points at a buffer that's always around, but the data is only updated when calcFFT() is called.
For the FFT to work, you also need to initialize SoLoud with the Soloud::
Soloud.getWave()
Gets 256 samples of the currently playing sound (post-clipping) and returns a pointer to the result.
float * wav = soloud.getWave();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++)
drawline(0, i, wav[i] * 32, i);
The returned pointer points at a buffer that's always around, but the data is only updated when getWave() is called. The data is the same that is used to generate visualization FFT data.
For this function to work properly, you also need to initialize SoLoud with the Soloud::
Soloud.getApproximateVolume()
Gets the approximate volume for output per output channel (i.e, per speaker). Returns zero for invalid parameters.
float ch1 = gSoloud.getApproximateVolume(0);
float ch2 = gSoloud.getApproximateVolume(1);
printf("Volume is %3.3f %3.3f", ch1, ch2);
Visualization needs to be enabled for this function to work.
Soloud.getVersion()
Returns the version of the SoLoud library. Same as SOLOUD_VERSION macro. Mostly useful when using the DLL, to check the DLL's library version.
if (soloud.getVersion() != SOLOUD_VERSION)
panic();
Soloud.getErrorString()
Converts SoLoud's error values to printable zero-terminated ascii strings.
int err = mod.load("foo.mod")
printf("Mod load:%s", soloud.getErrorString(err));
Soloud.setDelaySamples()
Sets number of samples to delay before starting to play a sound. This is used internally by the playClocked() function. In the unlikely event that you may want to use it manually, it's available in the public API.
h = soloud.play(snd, 1, 0, 1); // start paused
soloud.setDelaySamples(h, 44100); // delay for a second
soloud.setPause(h, 0); // go
Calling this on a "live" voice will cause silence to be inserted at the start of the next audio buffer. Since this is rather unpredictable (as audio buffer sizes may vary), it's not recommended, even if it may be a rather funky effect..
Soloud.getLoopCount()
Some sound sources that support looping also keep count of the loop count. This can be useful at least to detect when some sound loops.
int c = soloud.getLoopCount(h);
if (c != old_c)
printf("Looped!);
old_c = c;
Invalid handles and unsupported sound sources will cause the function to return 0.
Soloud.getInfo()
Some sound sources let you get real-time information from the active voice.
float reg10 = soloud.getInfo(c64song, 10);
If the call is not supported, or the handle is invalid, the function returns 0.
Soloud.getBackendId()
Get the current backend ID. This is typically the same as the Soloud::
printf("Current backend id: %d", gSoloud.getBackendId());
Soloud.getBackendString()
Get a printable asciiz string naming the current back-end. May return NULL.
if (gSoloud.getBackendString())
printf("Current backend: %s", gSoloud.getBackendString());
Soloud.getBackendChannels()
Get the number of channels the currently active backend plays.
printf("Current backend channels: %d", gSoloud.getBackendChannels());
1 for mono, 2 for stereo, various others for surround speaker setups.
Soloud.getBackendSamplerate()
Get the samplerate, in Hz, of the currently active backend. This may differ from the one requested.
printf("Current backend rate: %d", gSoloud.getBackendSamplerate());
Soloud.getBackendBufferSize()
Get the current backend's buffer size. May differ from the one requested. Some backends (such as PortAudio) may lie about this and use smaller buffer in reality.
printf("Current backend buffer: %d", gSoloud.getBackendBufferSize());
Soloud.setSpeakerPosition(), Soloud.getSpeakerPosition()
Get or set a speaker position in 3d space. Used to configure spakers in multi-speaker systems.
float x,y,z;
gSoloud.getSpeakerPosition(0, x, y, z); // get channel 0 speaker coordinates
gSoloud.setSpeakerPosition(0, 1.0f, 2.0f, 3.0f); // set channel 0 to play from (1,2,3)
For typical use these functions do not need to be called.
Copyright©2013-2020 Jari Komppa
